Software design
2025-10-29
Program architecture
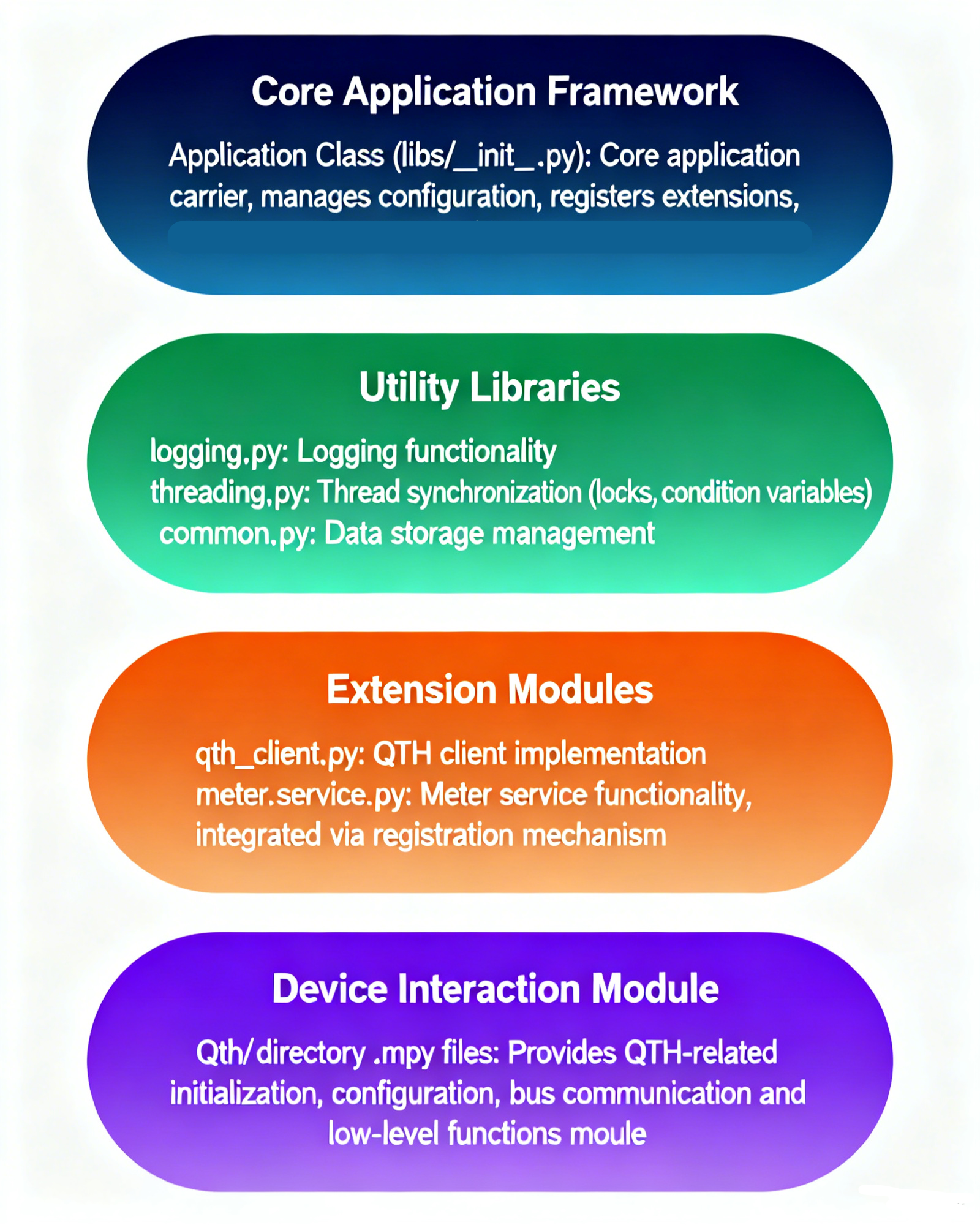
The software adopts a modular architecture design, mainly including four parts: core application framework, tool library, extension modules, and device interaction modules. Each module has clear responsibilities and low coupling, facilitating maintenance and expansion.
Business flow
Code details
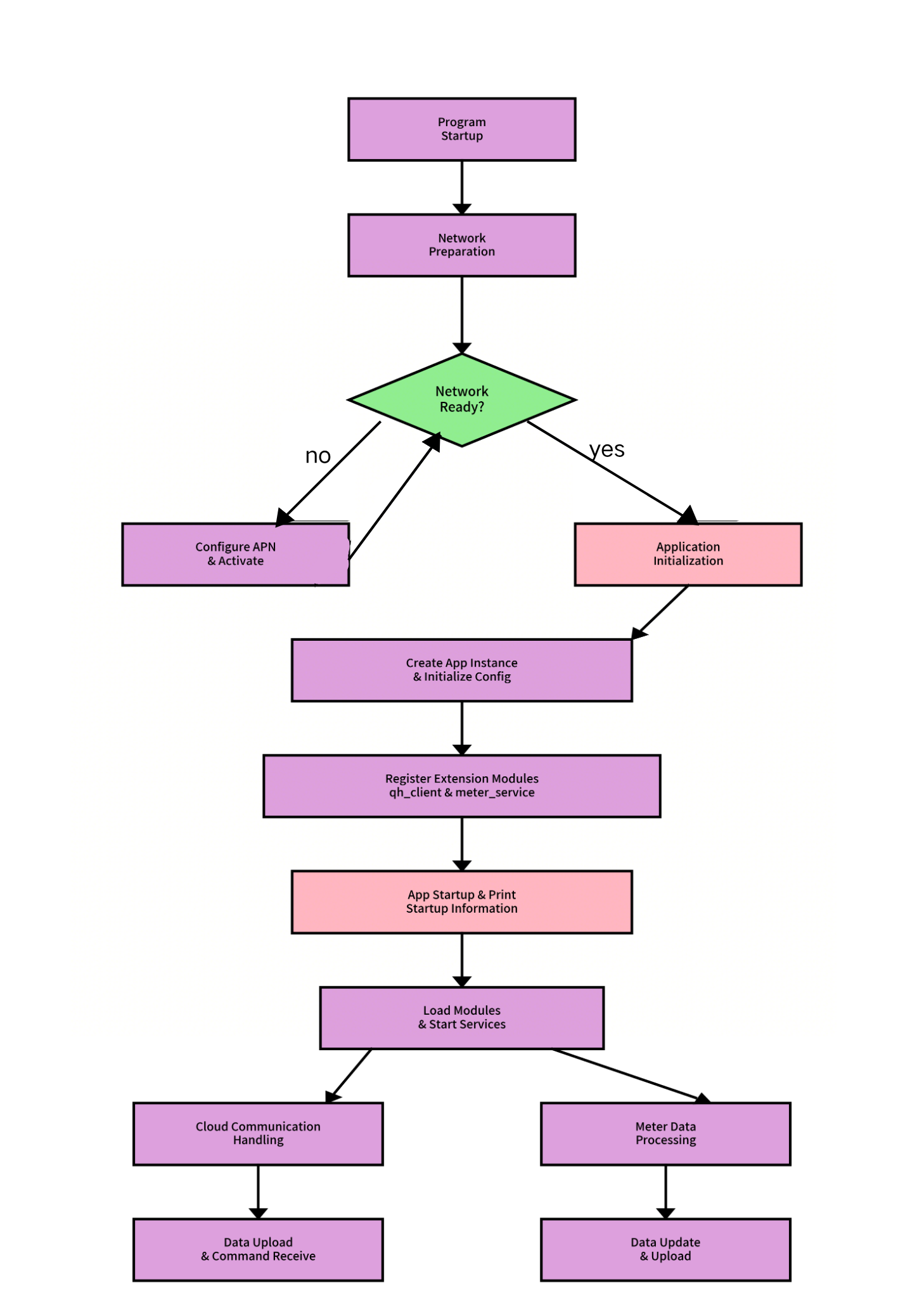
Program Entry _main.py Initialization Flow
_main.py is the program entry file responsible for network preparation, application creation, and startup. The specific flow is as follows:
- Network Waiting and Activation: Check network status through the
wait_network_readyfunction. If not ready, configure APN and activate.
def wait_network_ready():
wait_cnt = WAIT_NETWORK_READY_S / 5
is_ready = False
while wait_cnt:
lte = dataCall.getInfo(1, 0)
if lte[2][0] == 1:
is_ready = True
break
utime.sleep(5)
wait_cnt -= 1
return is_ready
if __name__ == "__main__":
while True:
if wait_network_ready():
logger.debug('lte network normal')
break
logger.debug('wait lte network normal...')
ret=dataCall.setPDPContext(1, 0, 'BICSAPN', '', '', 0)
ret2=dataCall.activate(1)
while not ret and ret2:
ret=dataCall.setPDPContext(1, 0, 'BICSAPN', '', '', 0)
ret2=dataCall.activate(1)
if ret and ret2:
print("Net injection failure")
break
- Application Creation and Initialization: The
create_appfunction initializes the application instance, loads configurations, and registers extension modules.
def create_app(name="meter_demo", version="1.0.0", config_path="/usr/config.json"):
_app = Application(name, version)
_app.config.init(config_path)
qth_client.init_app(_app)
meter_service.init_app(_app)
return _app
- Application Startup: After creating the application instance, call
app.run()to start the application, execute system information printing and extension loading.
app = create_app()
app.run()
QTH Client Uploading Data to Cloud
qth_client.py implements QTH client functionality, responsible for communicating with the cloud. The data upload process is as follows:
- Client Initialization: The
init_appmethod of theQthClientclass initializes QTH-related configurations and registers event callback functions.
def init_app(self, app):
app.register("qth_client", self)
qth_init.init()
qth_config.setProductInfo(app.config["QTH_PRODUCT_KEY"], app.config["QTH_PRODUCT_SECRET"])
qth_config.setServer(app.config["QTH_SERVER"])
qth_config.setEventCb(
{
"devEvent": self.eventCallback,
"recvTrans": self.recvTransCallback,
"recvTsl": self.recvTslCallback,
"readTsl": self.readTslCallback,
"readTslServer": self.recvTslServerCallback,
"ota": {
"otaPlan":self.otaPlanCallback,
"fotaResult":self.fotaResultCallback
}
}
)
- Data Sending Interface: Provides methods such as
sendTsl,sendLbs,sendGnssfor sending different types of data to the cloud. This solution only uses thesendTslmethod.
def sendTsl(self, mode, value):
return qth_bus.sendTsl(mode, value)
def sendLbs(self, lbs_data):
return qth_bus.sendOutsideLocation(lbs_data)
def sendGnss(self, nmea_data):
return qth_bus.sendOutsideLocation(nmea_data)
- Data Upload Trigger: When receiving a command to read data, generate random simulation data in the
readTslCallbackmethod and upload it through the relevant mechanism.
def readTslCallback(self, ids, pkgId):
logger.info("readTsl ids:{} pkgId:{}".format(ids, pkgId))
value=dict()
# Generate various meter data...
# Send generated data through QTH client
Meter Data Update Logic
The meter data update logic is mainly implemented in the readTslCallback method of qth_client.py. When receiving a command to read data, it generates random meter data as follows:
- Data Generation: Generate corresponding meter data according to different
id, including total electricity, phase voltage, current, power, etc. Some data is generated based on random functions.
def readTslCallback(self, ids, pkgId):
logger.info("readTsl ids:{} pkgId:{}".format(ids, pkgId))
value=dict()
# Combine total active energy and other random simulation data generation
com_total_active_energy = random_float(int(total_phase_a_energy + total_phase_b_energy + com_total_phase_c_energy), int(total_phase_a_energy + total_phase_b_energy + com_total_phase_c_energy), 2)
com_forward_active_energy = random_float(4500, 5500, 2)
com_reverse_active_energy = random_float(int(com_total_active_energy - com_forward_active_energy), int(com_total_active_energy - com_forward_active_energy), 2)
# Random simulation data generation for phase voltage, current, etc.
voltage_a = 220.0
current_a = random_float(9, 10, 2)
# ... Other phase data generation
# Map data according to id
for id in ids:
if 1 == id:
value[1]=True
elif 2 == id:
value[2]=random_float(6000, 6600, 2)
# ... Mapping of other id corresponding data
- Data Update Trigger: When the cloud or other modules trigger a command to read data, the
readTslCallbackmethod is called to generate the latest random data, realizing dynamic update of meter data.
