Home NAS Server User Manual
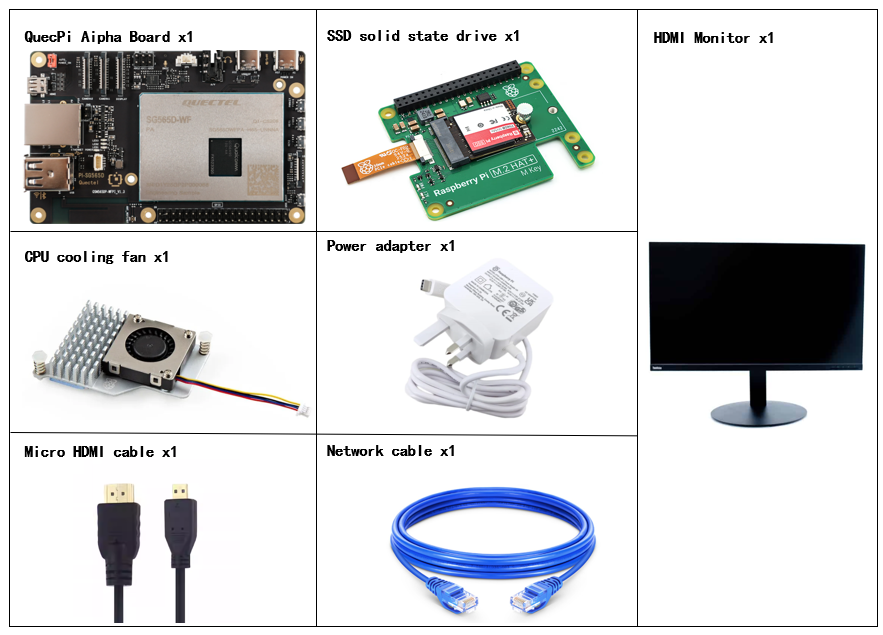
Development Kit Accessories List
| Component Name | Quantity | Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| PI-SG565D Single Board Computer | 1 | Quectel PI-SG565D Smart Ecosystem Development Board for Linux Learning with Python Programming and AI Kit For more specs, refer to PI-SG565D Product Page |
| USB-A Power Adapter | 1 | Power Adapter |
| USB-C DP Cable / HDMI Cable | 1 | DP 1.4 spec; Length: 1m; USB-C (male) to USB-C (male) HDMI 2.0 spec; Length: 1m; HDMI-A (male) to HDMI-D (male) |
| Ethernet Cable | 1 | Length: 1m; Gigabit transmission rate |
| SSD Solid State Drive | 1 | Official Raspberry Pi SSD Kit |
| CPU Cooling Fan | 1 | Raspberry Pi 5 Official Active Cooler with Heatsink and Thermal Pad |
| Display Screen | 1 | HDMI Monitor |
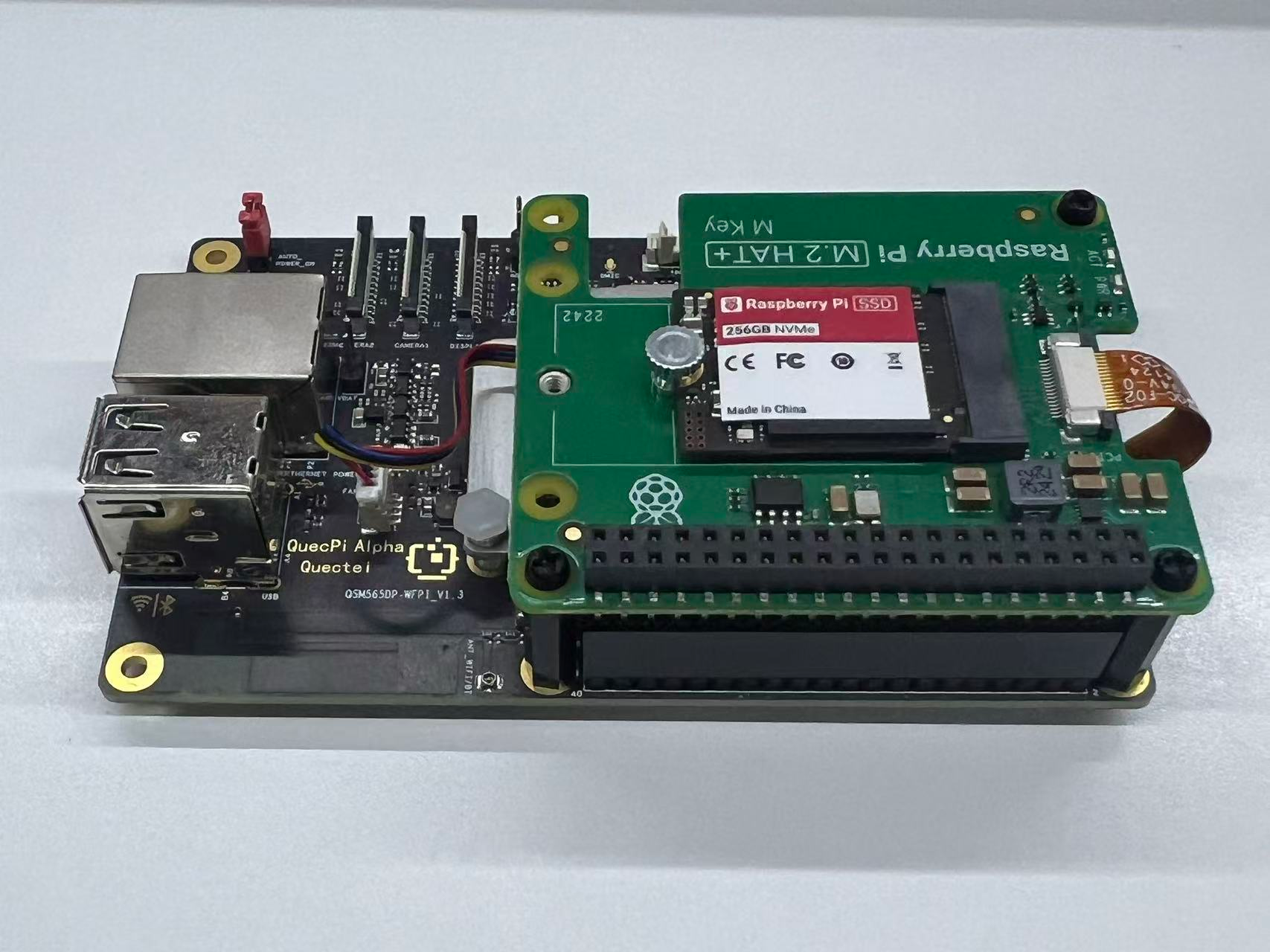
Reference Image of Accessories
Development Setup
The PI-SG565D comes pre-installed with Debian 13, so no re-flashing is required. Just follow the steps below:
Hardware Connection Steps
Install CPU Cooling Fan: Plug the fan cable into the FAN header on the board, then secure the heatsink clips into the mounting holes as shown:
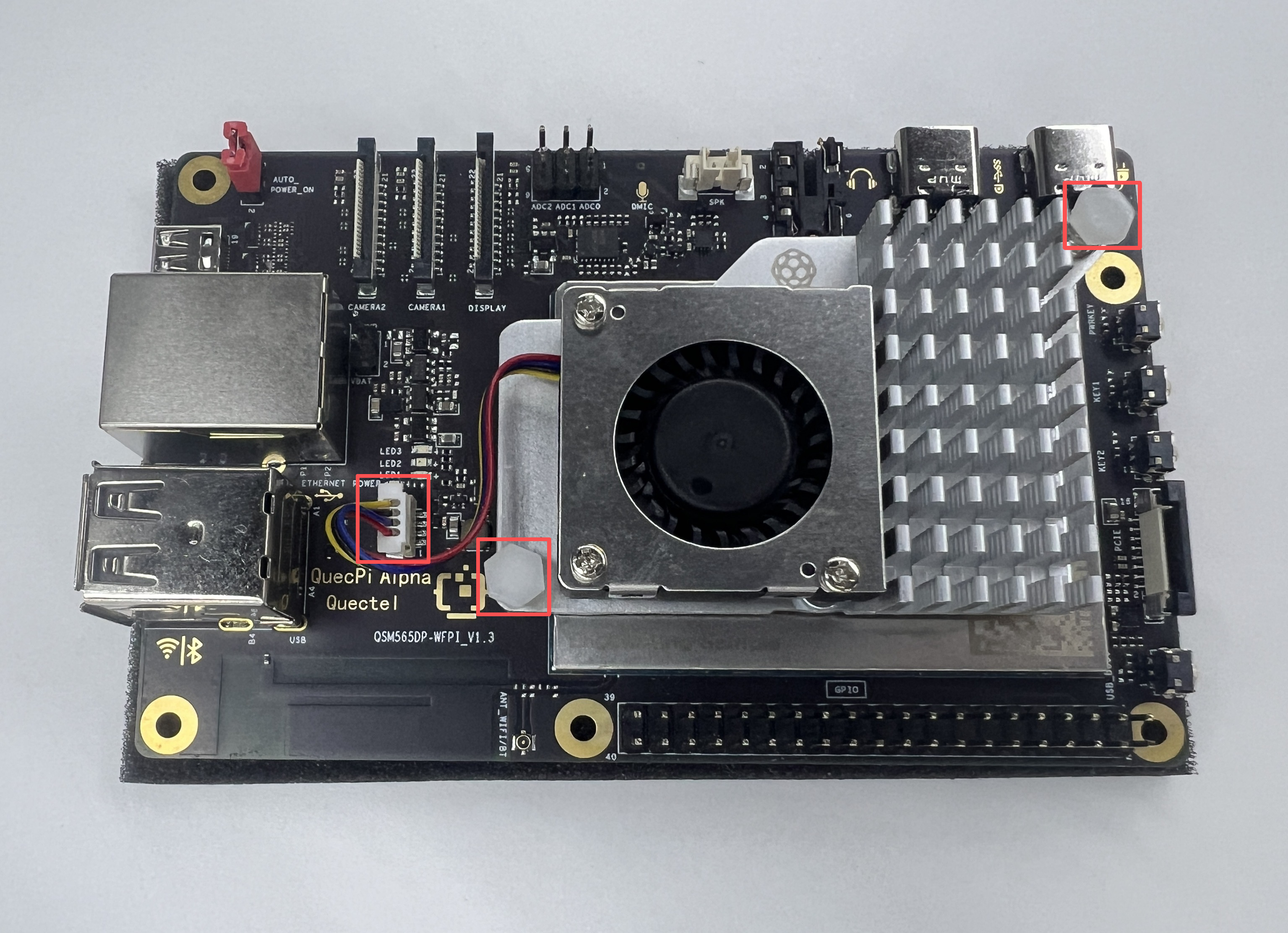
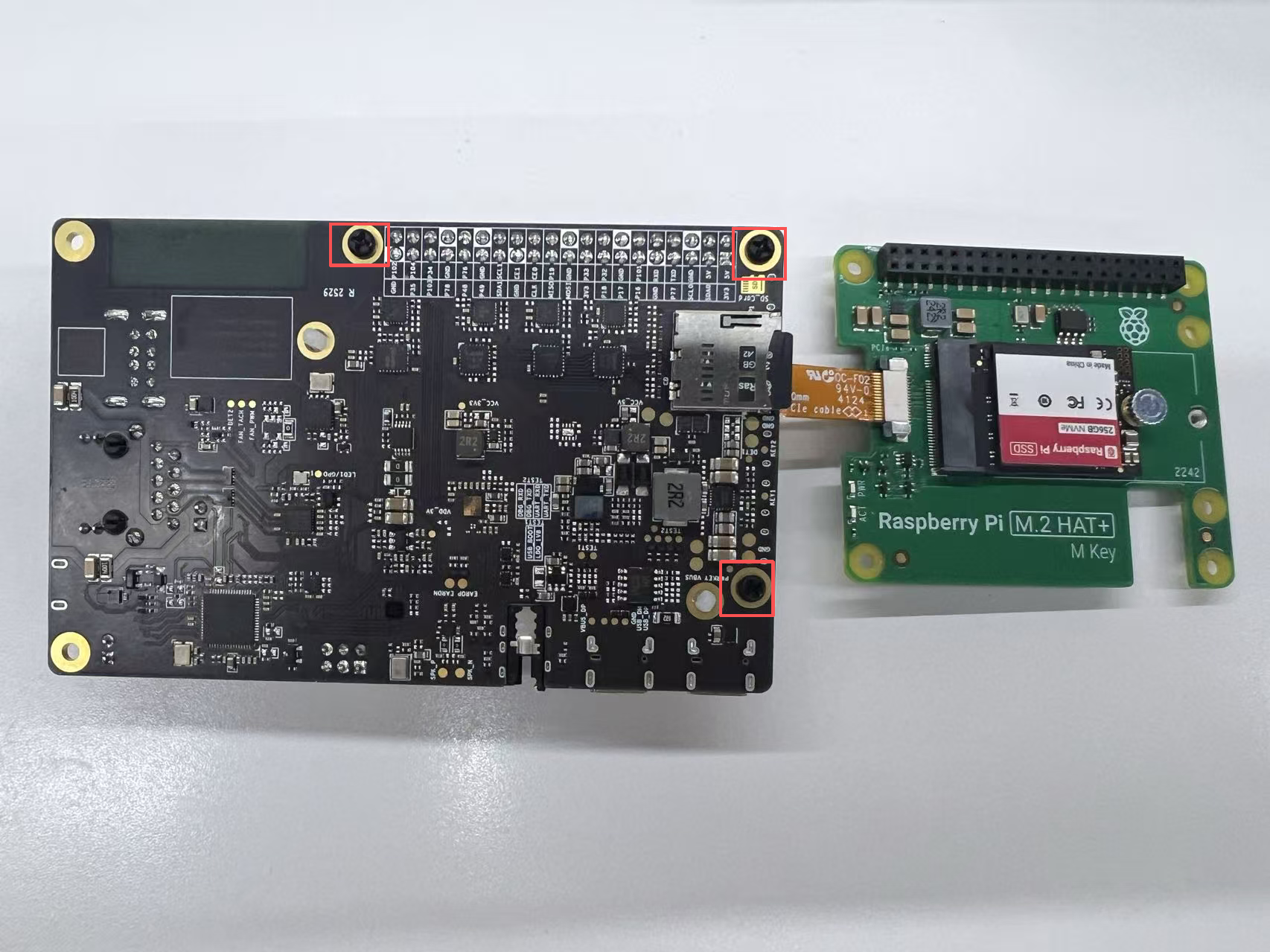
- Install SSD:
- Install 3 nylon standoffs using short screws.
- Attach the GPIO adapter firmly.
- Insert the PCIe ribbon cable into the board’s PCIe slot and secure both sides.
- Place the M.2 HAT+ on top and secure it with 3 long screws.
Front view after installation:

Back view:

Side view:

Finally, place the M.2HAT+ on top of the nylon post and use the remaining 3 long screws to secure the M.2HAT+ in place.
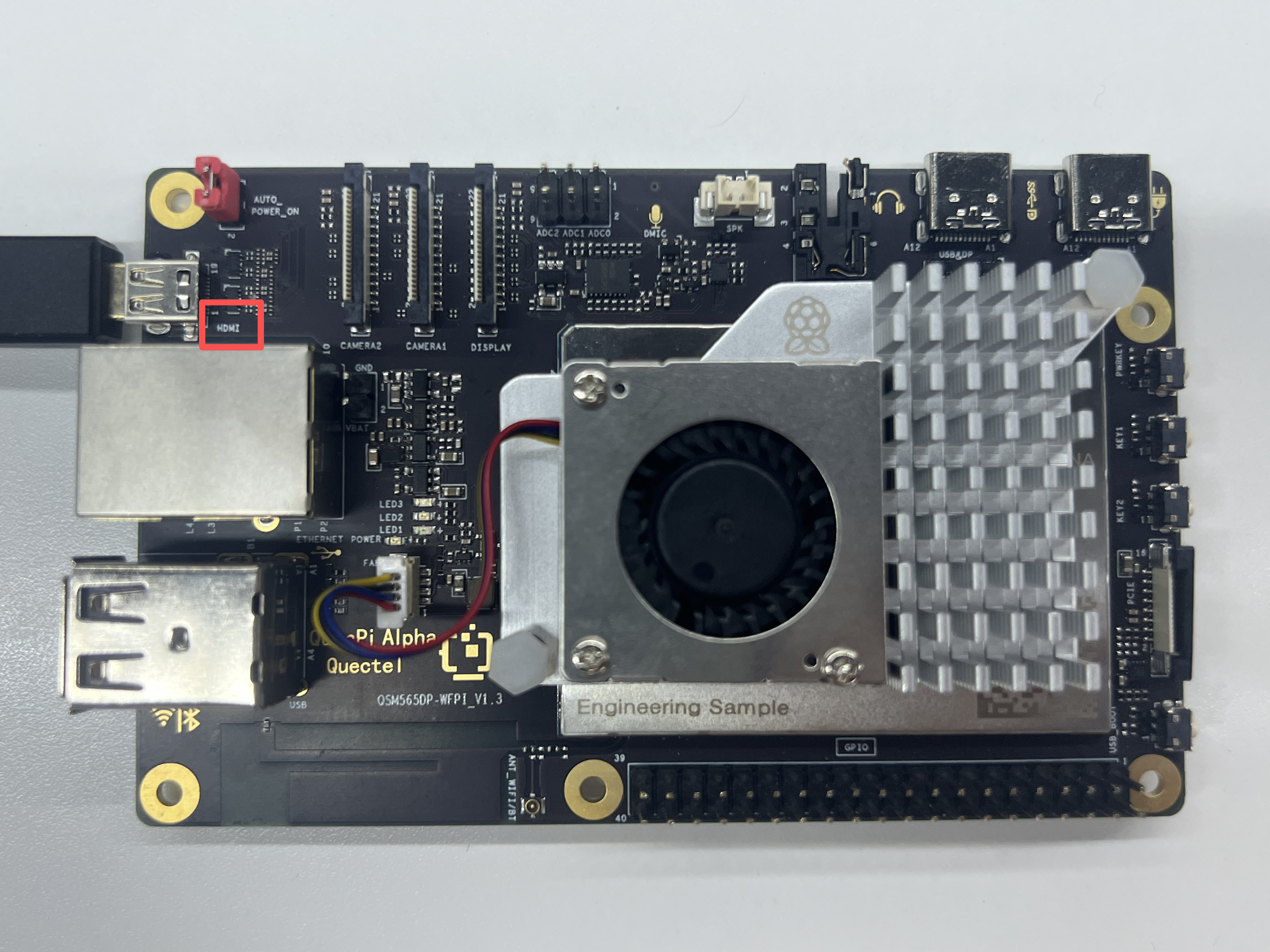
- Display Connection:Connect one end of the HDMI cable to the HDMI port of the single-board computer and the other end to the HDMI port of the monitor.
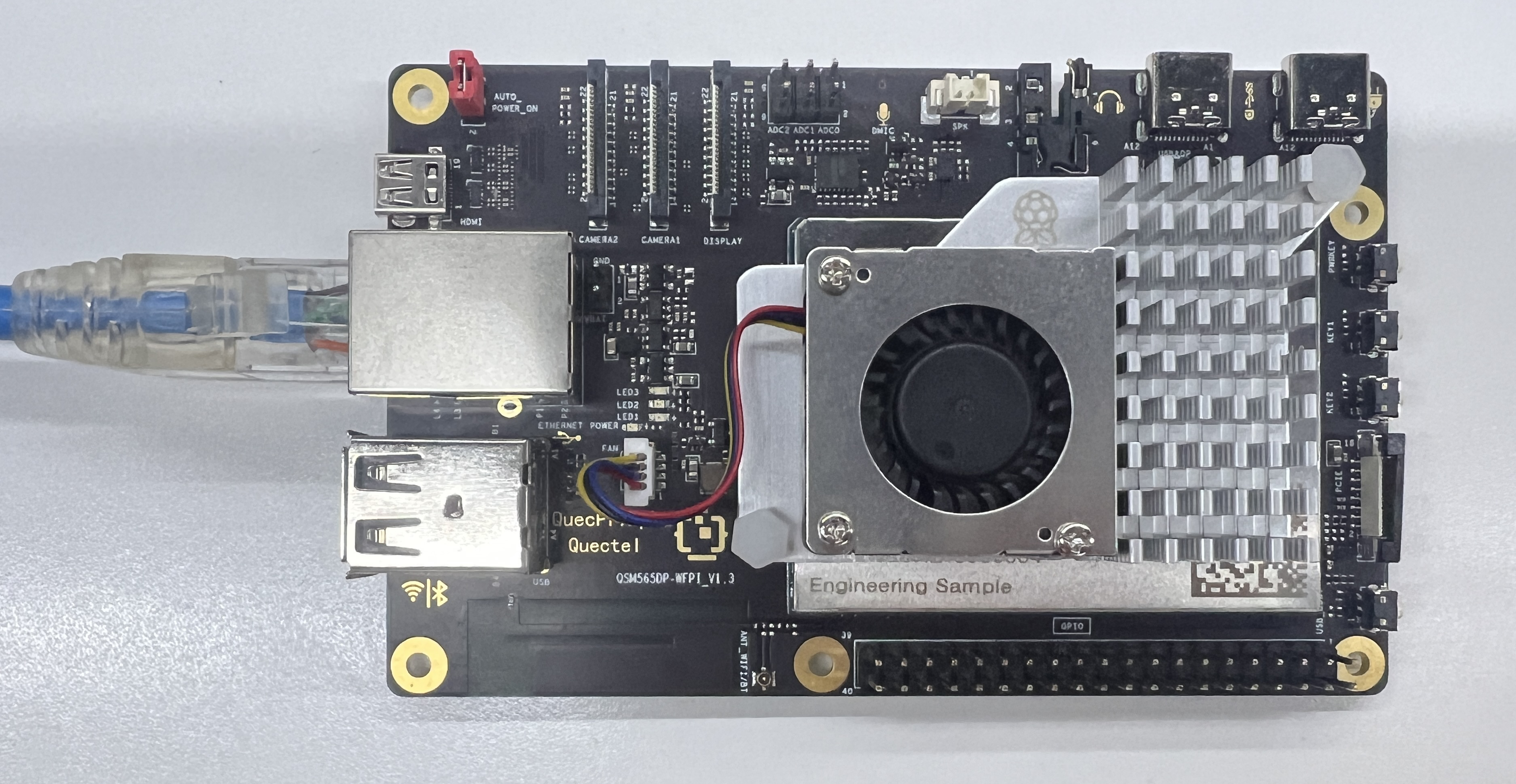
- Input Devices: Plug USB keyboard/mouse into the USB-A ports. Wireless dongles also supported.

- Network: Connect Ethernet cable from board to router (ensure internet access).
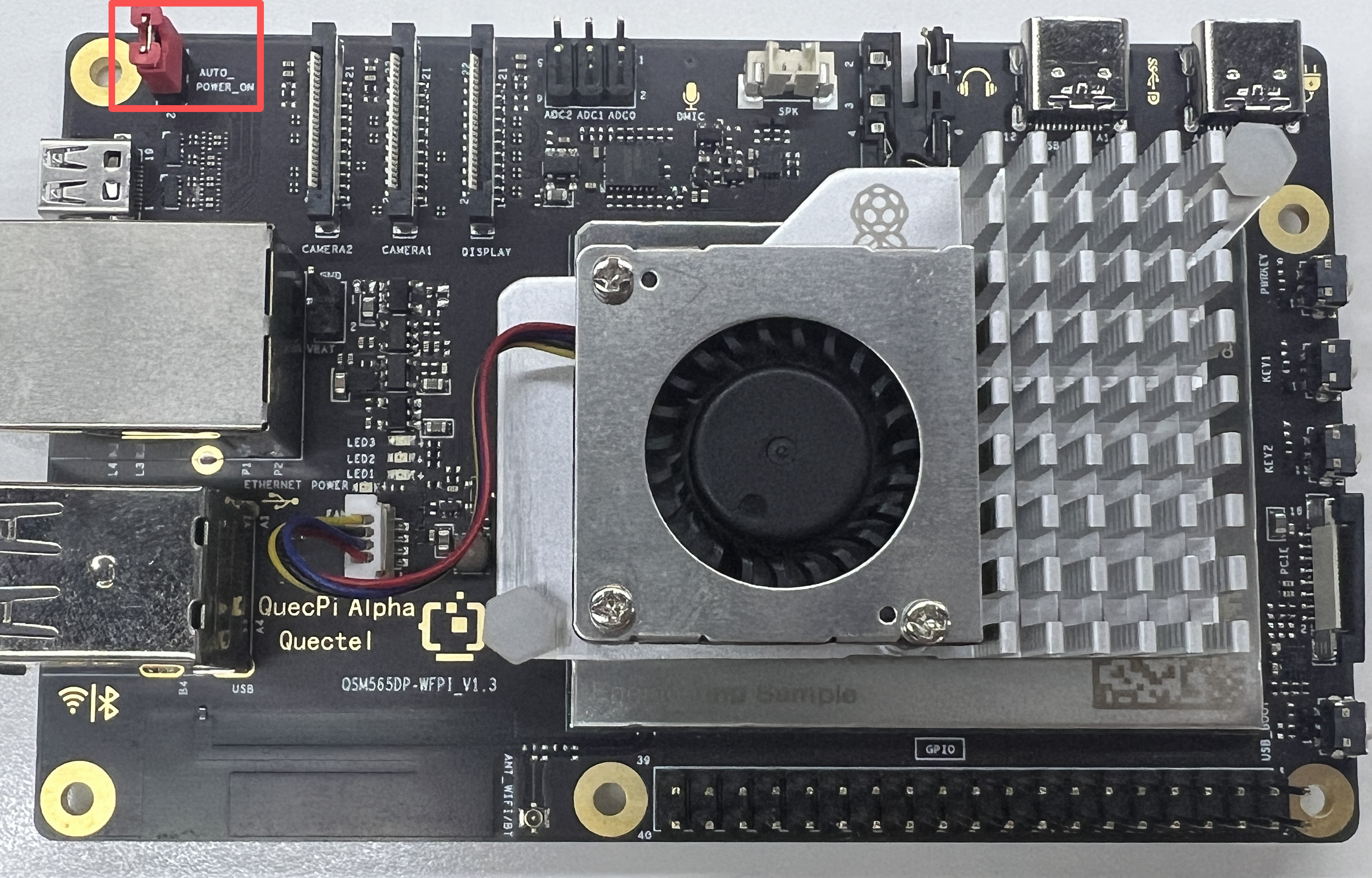
- Jumper: Ensure the AUTO_POWER_ON pins are shorted with a jumper cap.
- Power: Connect USB-A power adapter to the POWER IN port.
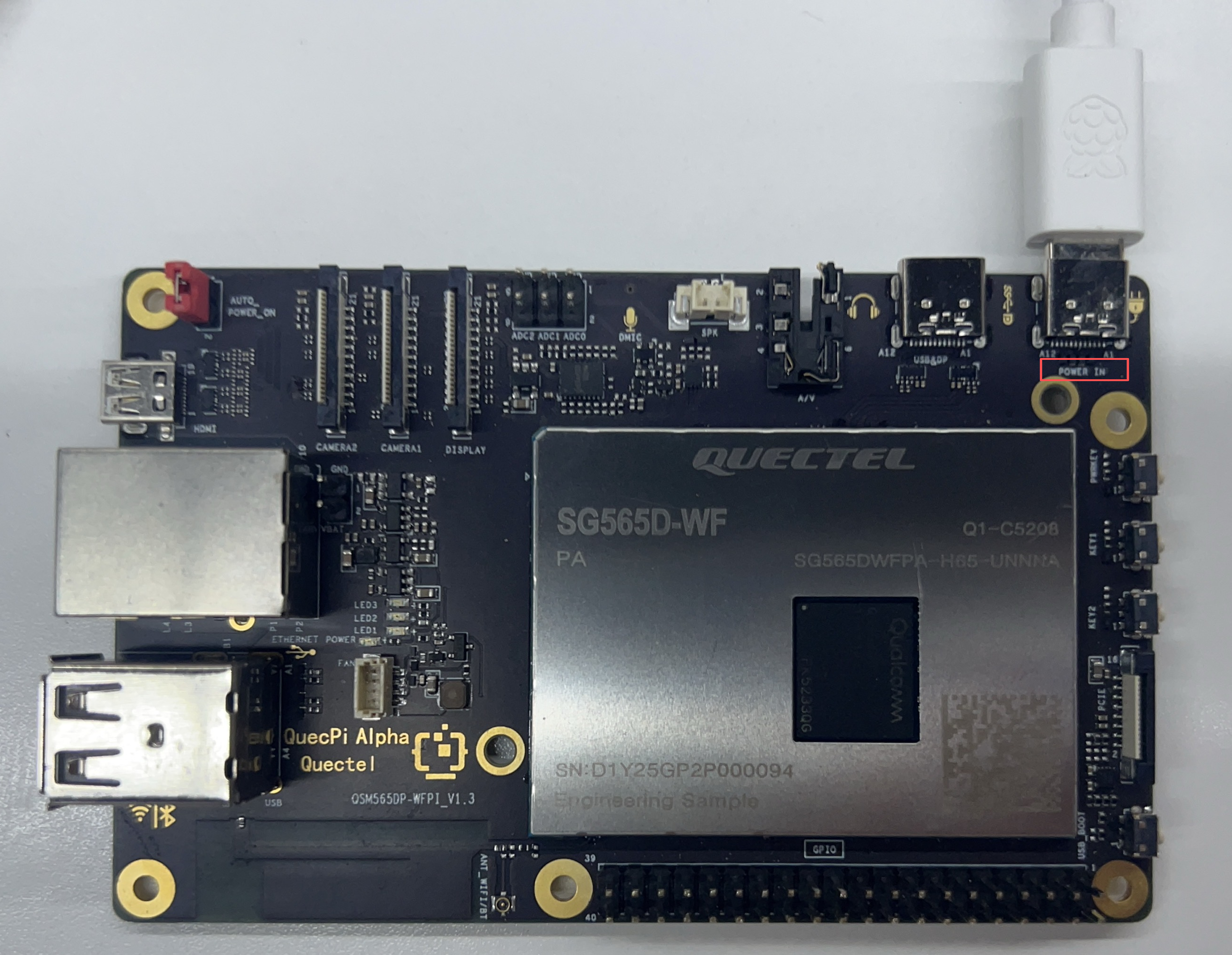
- Final setup reference:
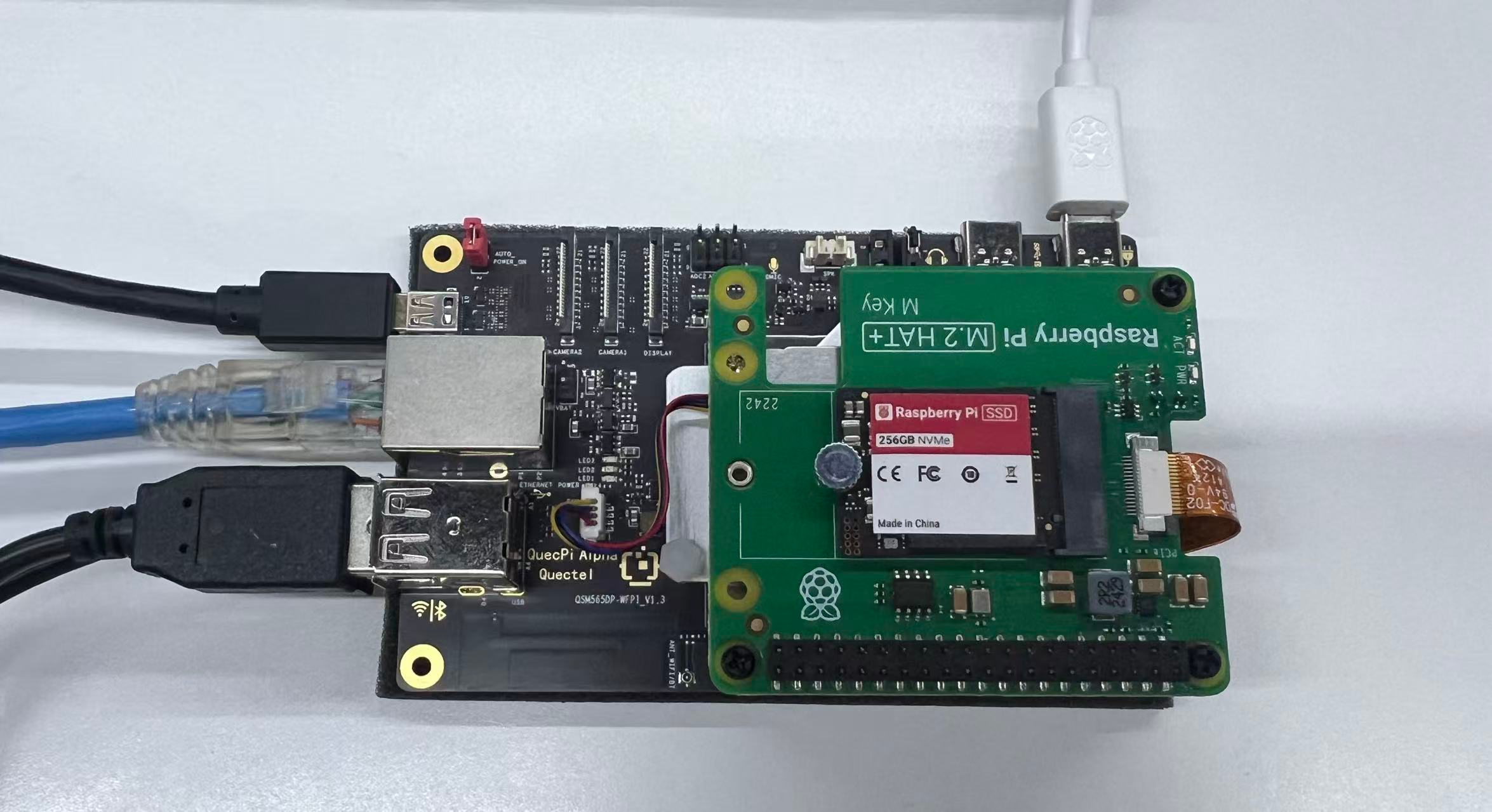
Implementation Steps
- Update package list
sudo apt-get update
- Install Samba
sudo apt-get install samba
- Create mount folder
sudo mkdir /mnt/resource
- Set permissions
sudo chown -R username: /mnt/resource/
- Check disk info
1.List partitions
awk 'NR > 2 {printf "%-10s %s\n", $4, $3 / 1024 / 1024 " GB"}' /proc/partitions
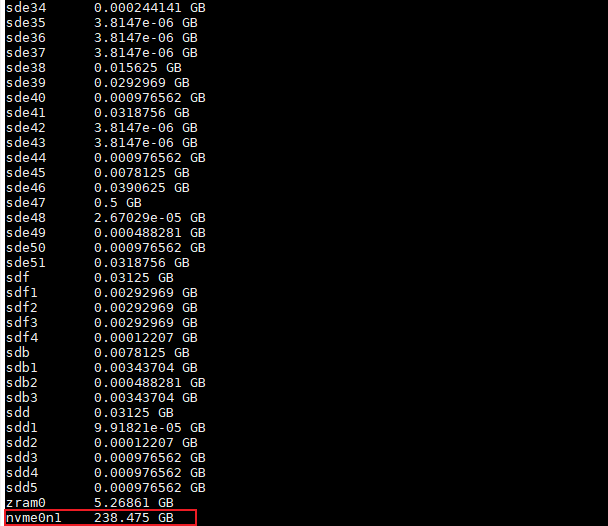
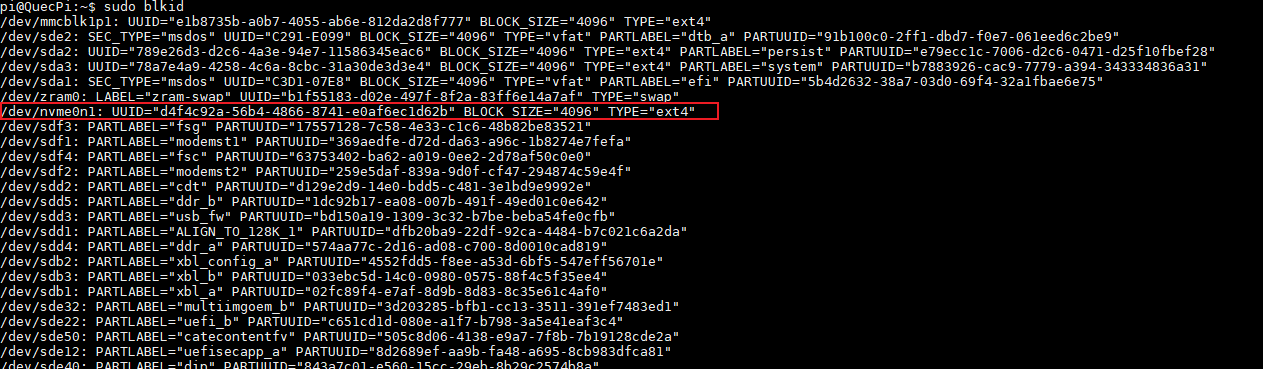
2.Check filesystem type(Note: The PI-SG565D board is mounted with ext4 by default, If the file type of the external storage device does not match the system, the storage device needs to be reformatted.)
sudo blkid
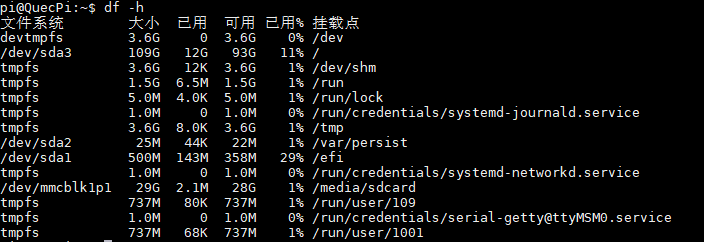
3.Check current mounts(If there is a mount point under /mnt/resource, you need to uninstall the mount point first)
df -h
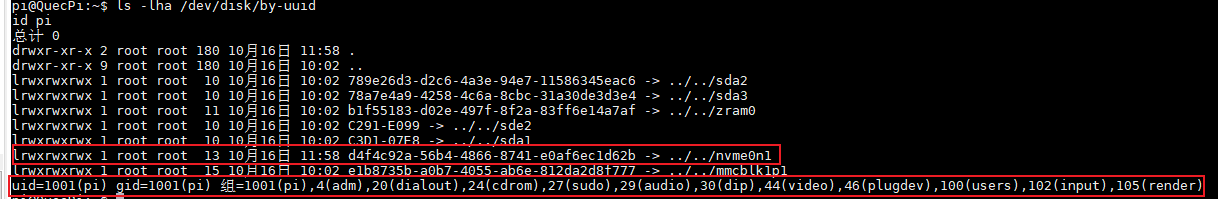
4.Get UUID and user UID/GID
ls -lha /dev/disk/by-uuid
id username
- Edit
/etc/fstab
Here we use a 256GB solid-state drive as the NAS server, so we select nvme0n1 as the extended partition to mount and modify the fstab file.
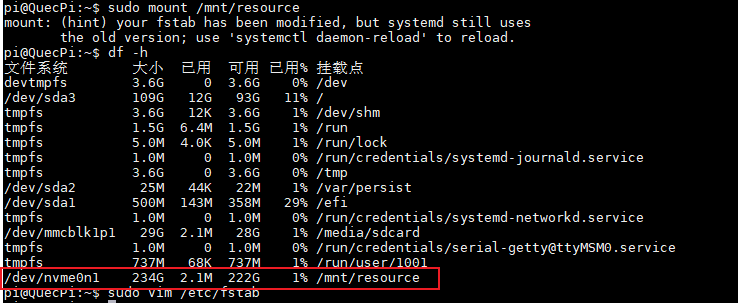
sudo vim /etc/fstab
Add the following statement at the end of the file. After adding, press ESC+":" and then enter wq and press Enter to save and exit.
#Use ext4 as the file system, refer to the partition file type found in the previous step.
#Add the nofail option. The nofail option allows normal booting even if the device does not exist.
UUID=The UUID queried in the previous step /mnt/resource ext4 defaults,nofail 0 0

- Mount the drive
sudo mount /mnt/resource
- Configure Samba user
sudo smbpasswd -a username
Note: Enter the current user name and password. Please note that the user here must be an existing Linux user.
- Edit Samba config
Enter the following command to open the configuration file
sudo vim /etc/samba/smb.conf
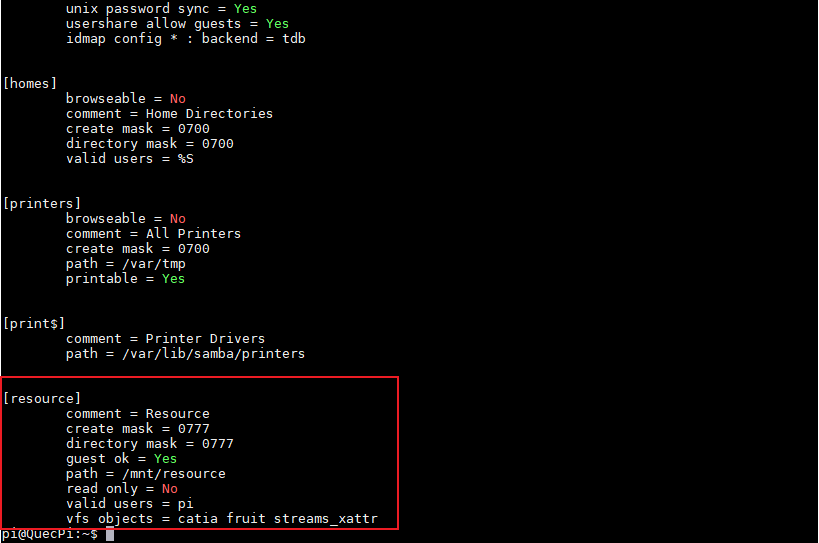
Add(The disk name in brackets is displayed externally)
[resource]
comment = Resource
create mask =0777
directory mask = 0777
path = /mnt/resource
valid users = pi
read only = no
vfs objects = catia fruit streams_xattr
- Test config
sudo testparm -s
- Restart Samba
sudo systemctl restart smbd
sudo systemctl enable smbd
- Test access
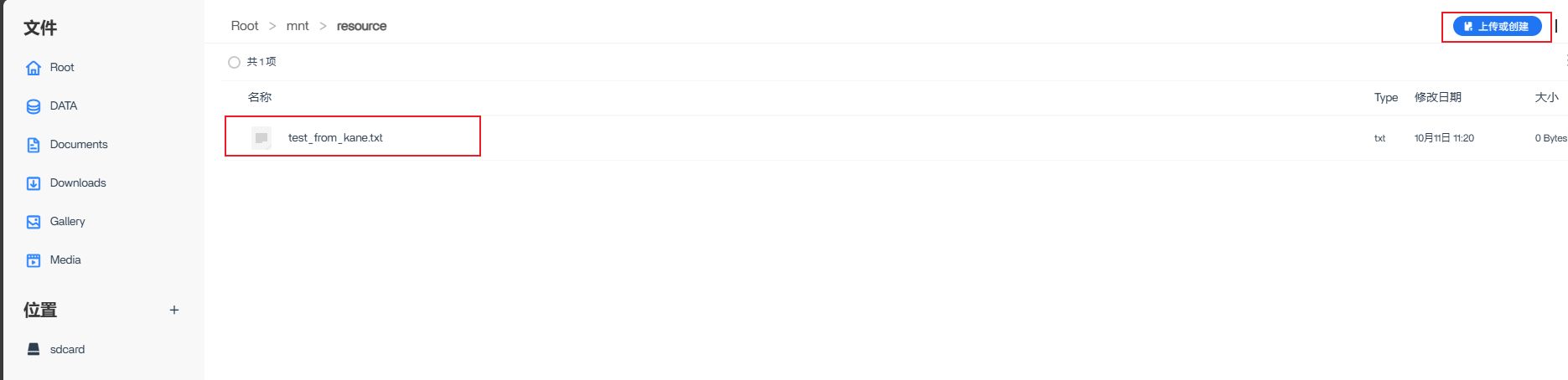
sudo -u username touch /mnt/resource/test_from_kane.txt
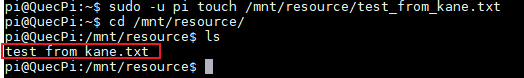
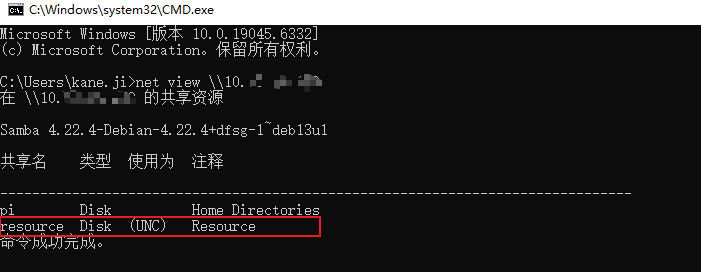
- Test from Windows CMD
net view \\[NAS_IP]
Connecting to the NAS
Windows File Explorer (Easiest)
Set full permissions.
cd /mnt
sudo chmod 777 resource/
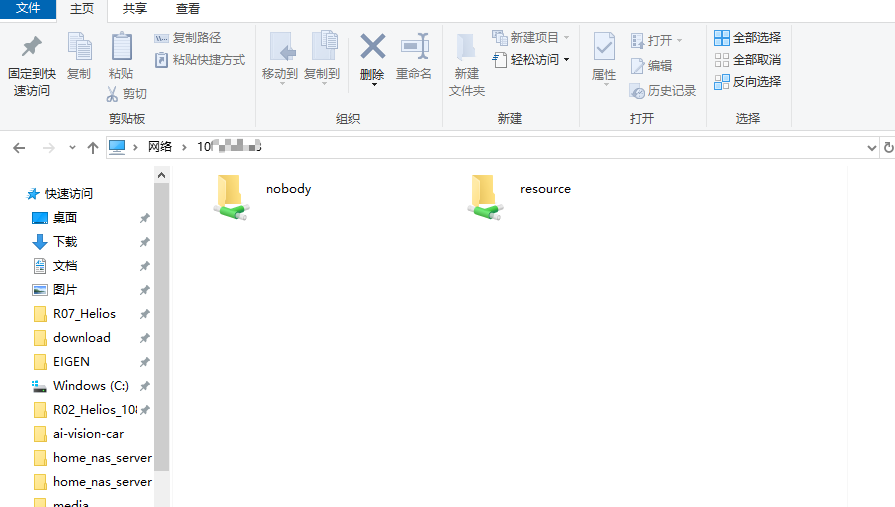
Get NAS IP.
In Windows Explorer, input"\\ <NAS_IP>",You’ll see shared folders.
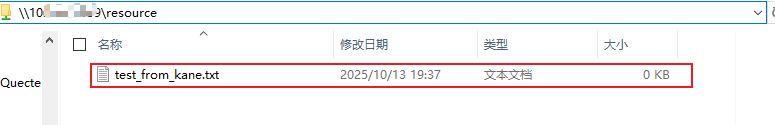
- Open
resourceto add/delete/edit files.
SCP Commands
Upload files from Windows to NAS server.
scp "local_file_path" username@nas_ip:/mnt/resource/
- Upload an entire folder to the NAS server from Windows.
scp -r "local_folder_path" username@nas_ip:/mnt/resource/
CasaOS Web Access
Add GPG key
#1. Open the image source file
sudo vim /etc/apt/source.list
#2. Add mirror source
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/debian trixie main contrib non-freeeeee
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/debian trixie-updates main contrib non-freefree
deb https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/debian-security trixie-security main contrib non-free
#3.Enter the following command in the console to add the GPG key of the software source
echo \ "deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/debian \ $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
#4.Update the installation source after adding and saving
sudo apt update
- Configuring iptables Rules
Check the current iptables version. If "no alternatives for iptables" appears, you need to install iptables-legacy.
sudo update-alternatives --config iptables
After entering the command, it displays:
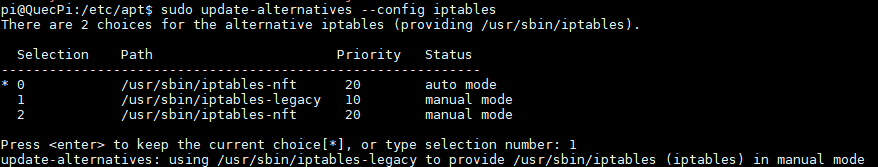
You can see that our Pi development board is using the iptables-nft policy. Enter 1 (corresponding to /usr/sbin/iptables-legacy) in the console prompt and press Enter.
Similarly, enter the following command to enable ip6tables. Enter 1 (corresponding to /usr/sbin/ip6tables-legacy) in the console prompt and press Enter to complete the configuration.
sudo update-alternatives --config ip6tables
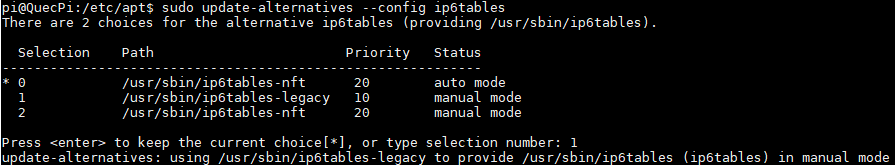
- Check the current iptables version
sudo iptables --version
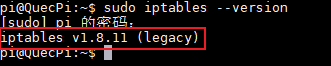
Displaying the version number of iptables-legacy proves that the policy is effective.
- Install Docker
sudo apt install docker.io
- Start the Docker service
sudo systemctl start docker
sudo systemctl enable docker
- Check Docker service status
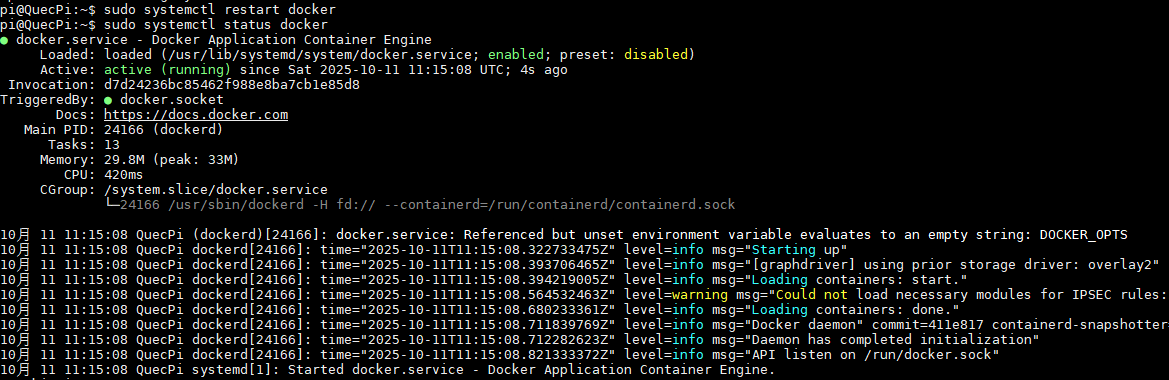
sudo systemctl status docker
After successful startup, the following is shown:
- Full installation of wget
sudo apt install wget -y
When the following option box appears, just press Enter.
- Install CasaOS
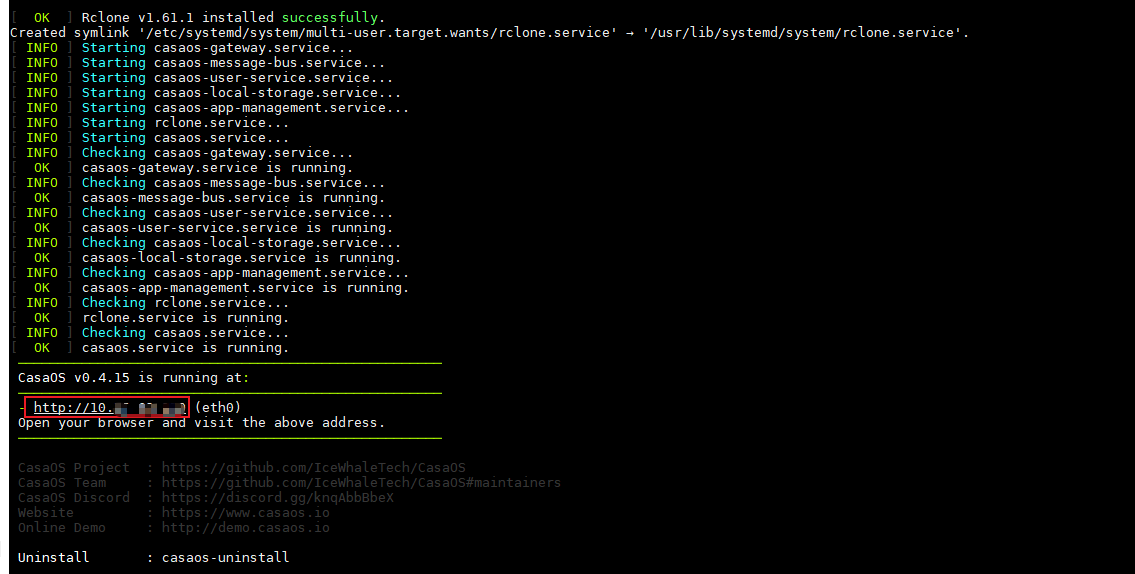
curl -fsSL https://get.casaos.io | sudo bash
After successful installation, copy the URL in the red box and open it in the browser.
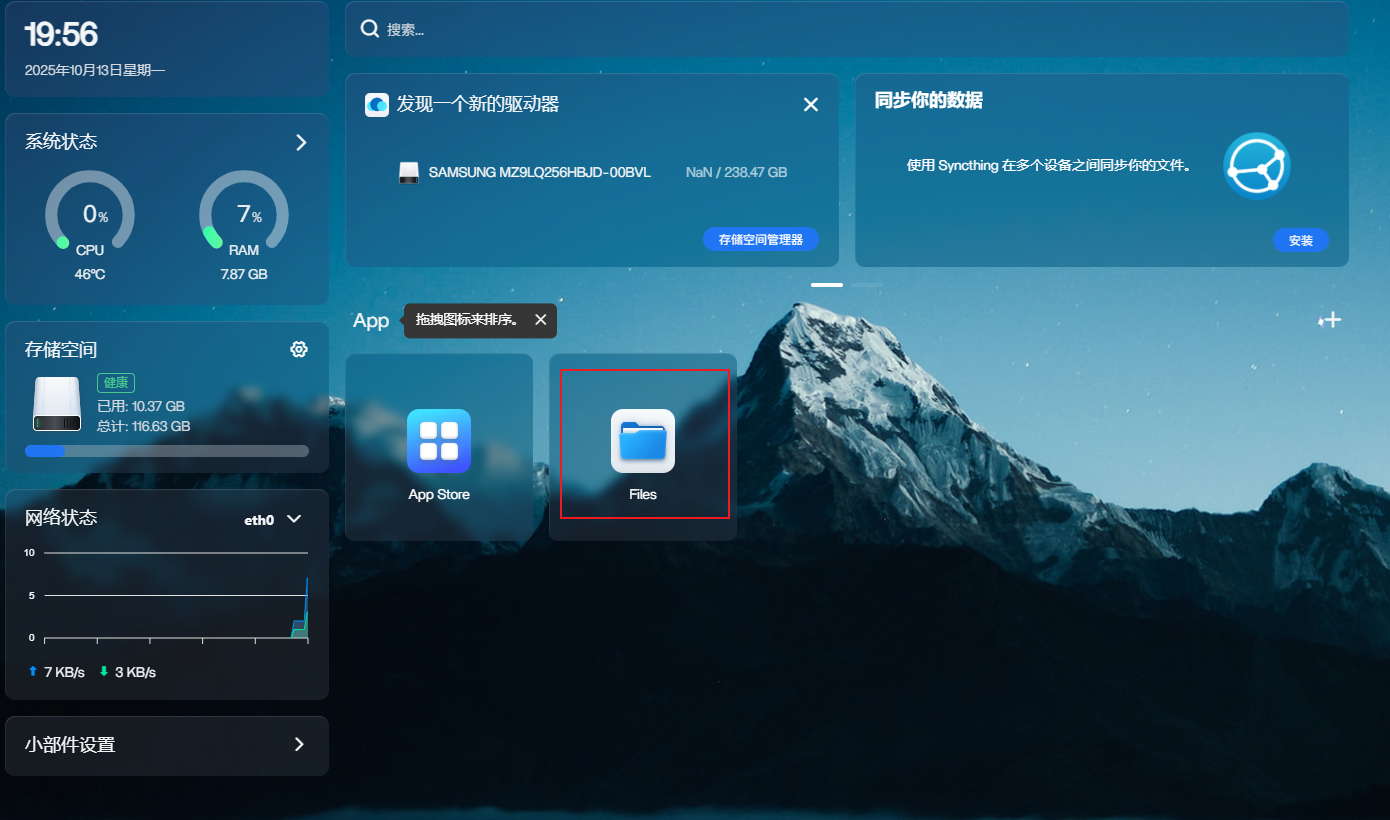
After creating a user, log in and click Files. After finding the folder mounted on the NAS server in the Root directory, you can directly upload, delete, modify, etc.